In the fields of industrial solid waste treatment and resource recycling, shredder selection must closely match the material characteristics. As the core model in the shredder family, specializing in processing tough, flexible materials, the single-shaft shredder, with its unique "single spindle + fixed blade" design, offers irreplaceable performance advantages in shredding easily entangled materials such as plastic film, woven bags, and waste fabric. While single-shaft shredders have limitations in shredding hardness and processing volume compared to multi-shaft shredders like dual-shaft and quad-shaft shredders, their outstanding performance in particle size, maintenance costs, and ease of operation make them a specialized piece of equipment in this niche market. This article will systematically analyze the core structure of the single-shaft shredder, systematically analyzing its technical features. Furthermore, by integrating practical application scenarios, it will delve into its core advantages in industrial production, providing a selection guide for companies seeking to shred tough materials.
Core Structure and Technical Features of Single-Shaft Shredders
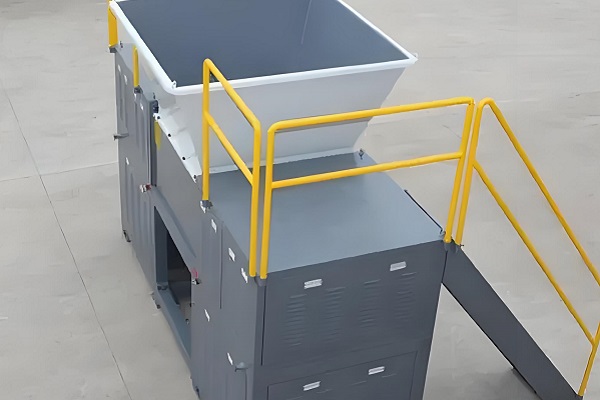

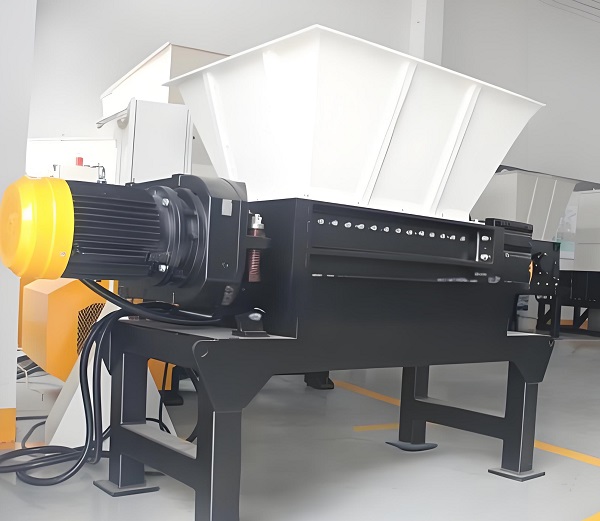
The performance advantages of single-shaft shredders stem from their streamlined and efficient structural design. The core components are a single rotating main shaft, fixed blades, a pusher, a crushing chamber, a drive system, and a control system. This "single-shaft main shaft + fixed blade" structure creates unique technical features that distinguish it from multi-shaft shredders. These features can be summarized in the following five aspects:
1. The "single-shaft + fixed blade" shearing structure specializes in easily entangled materials.
The core structural feature of a single-shaft shredder is its use of a horizontally arranged rotating main shaft. A spirally arranged rotating blade (cutter head or blade head) is secured to the main shaft surface via keyways and bolts. A fixed fixed blade is mounted on the inside of the housing, corresponding to the rotating blade. A precise gap of 0.5-5mm is maintained between the rotating and fixed blades. The drive system, via a reduction motor and gearbox, drives the main shaft (typically at 50-150 rpm). Once the material enters the crushing chamber, a pusher (mostly hydraulically driven) continuously pushes it toward the meshing area between the rotating and fixed blades. The rotating shearing action of the rotating blade and the fixed support of the fixed blade achieve a dual crushing effect: shearing and tearing.
This structure is particularly advantageous for handling materials prone to entanglement. For materials prone to entanglement, such as plastic film, woven bags, and waste fabric, the spiral blades of a single-shaft shredder utilize a "gradual gripping and directional conveying" mechanism to gradually shear the material from the inlet to the outlet, preventing it from entanglement. For example, when handling plastic film, the spiral blades pull the film into the shearing area, shredding it and discharging it through the outlet, eliminating the risk of entanglement. In a dual-shaft shredder, the counter-rotating shafts can easily cause the film to entangle between the shafts, requiring frequent downtime for cleaning.
2. Spiral blade assembly and precise clearance design ensure high particle uniformity
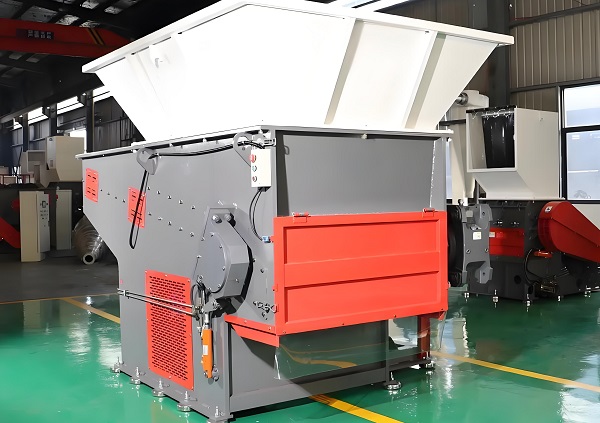

Single-shaft shredders often use a spiral arrangement of the rotating blades. The blade discs (or blade heads) are arranged in a spiral pattern along the main shaft axis, which, combined with the fixed position of the stationary blades, form a continuous "cutting line." Furthermore, the gap between the rotating and stationary blades can be precisely controlled (down to 0.5mm) using an adjustment bolt, ensuring uniform particle size with every cut. This design ensures that single-shaft shredders achieve significantly higher particle uniformity than twin-shaft shredders. Data shows that particle size deviation in single-shaft shredders is typically ≤±1mm, while twin-shaft shredders often achieve particle size deviations exceeding ±3mm.
For example, in the pre-processing stage of plastic recycling pelletization, the size of the resulting plastic pellets must be uniform (typically 3-5mm). Otherwise, melt uniformity in the subsequent pelletization process will be compromised. Single-shaft shredders, by adjusting the blade gap to 3mm, can shred plastic bottles and plastic sheets into uniform particles. These particles can then be fed directly to the pelletizer without subsequent screening. However, the plastic pellets shredded by dual-shaft shredders often contain large pieces of material larger than 10mm, requiring an additional screening step, increasing production costs and time.
3. Simplified Structure, Low Maintenance Cost and Difficulty
Compared to the complex multi-shaft drive systems of dual-shaft and quad-shaft shredders, single-shaft shredders feature a more streamlined structure—requiring only one main shaft, one set of rotating blades, and one set of fixed blades. The drive system involves only one reduction motor and gearbox, reducing points of failure and the number of maintenance components. This is reflected in the following two aspects:
Easy and Low-Cost Blade Maintenance: The rotating blades of single-shaft shredders feature a modular, removable design. The blade heads can be individually removed and replaced when worn, eliminating the need to replace the entire blade assembly. For example, when processing plastic materials, the blade life of a single-shaft shredder is approximately 3-6 months. Each replacement only requires replacing the worn blades (a single set of blades costs approximately 500-2000 yuan), while a dual-shaft shredder requires replacing worn blades on both sets of blade discs, costing approximately 2000-8000 yuan. Furthermore, blade replacement for a single-shaft shredder requires only one to two people, taking one to two hours, while a dual-shaft shredder requires two to three people, taking three to four hours.
The drive system is simple to maintain: The drive system of a single-shaft shredder only requires regular checks of the operating status of one motor and the lubrication level of one gearbox. There's no need to synchronize the speed and torque of multiple motors, as is required with multi-shaft shredders. Statistics show that the average annual maintenance cost of a single-shaft shredder is approximately 50%-70% of that of a dual-shaft shredder, and downtime for maintenance is approximately 40%-60% of that of a dual-shaft shredder.
4. Low-speed, high-torque, and overload protection ensure strong operational stability.
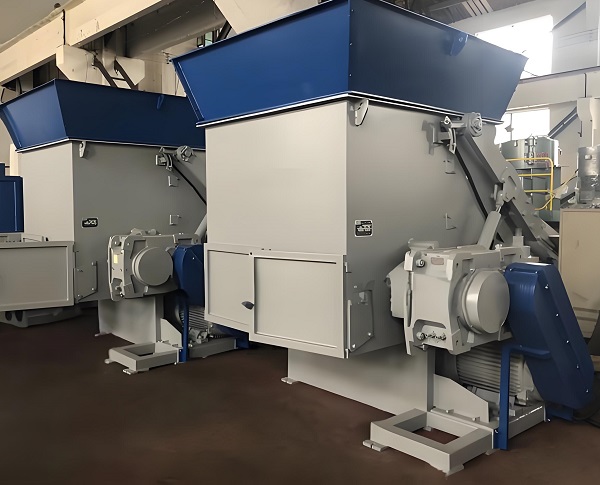

Although the main shaft speed of a single-shaft shredder (50-150 rpm) is higher than that of a dual-shaft shredder (20-60 rpm), its "high-reduction-ratio gearbox" design achieves "low-speed, high-torque" operation. Torque typically reaches 1000-5000 N·m, sufficient to handle the shredding of tough materials. Single-shaft shredders are also equipped with a comprehensive overload protection system, including the following:
Hydraulic pusher overload protection: When material hardness exceeds a set value (e.g., if small metal pieces are mixed in), the hydraulic system of the pusher automatically releases pressure and stops pushing, preventing damage to the movable and fixed blades due to excessive force.
Motor current monitoring protection: The control system monitors the motor current in real time. If the current exceeds the rated value (e.g., if excessive material load increases the spindle), the machine automatically shuts down and issues an alarm.
Spindle reversal function: Some high-end single-shaft shredders are equipped with a spindle reversal function. If material becomes stuck in the shearing area, the spindle rotates in the opposite direction, pushing the material out of the crushing chamber and eliminating manual disassembly and cleaning.
These protective measures significantly reduce the failure rate of single-shaft shredders when processing tough materials, achieving an effective operating time of over 90%. For example, in textile waste recycling projects, when a single-shaft shredder is processing waste fabric, even if a small amount of sewing needles are mixed in, the machine will immediately shut down due to overload protection, remove the debris, and resume operation, preventing damage to the blades.
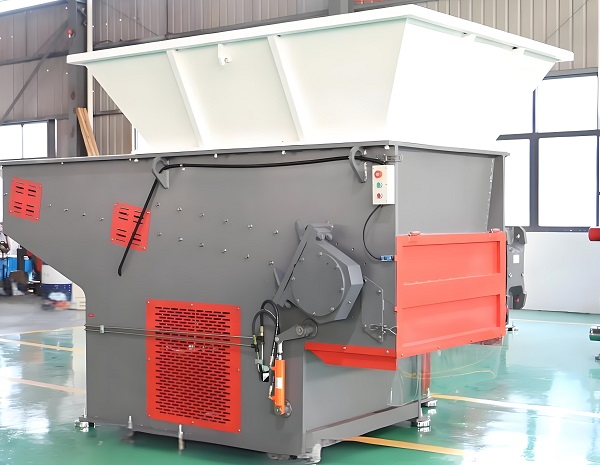
5. Compact Size and Flexible Layout, Suitable for Small Spaces
The streamlined structure of a single-shaft shredder makes it significantly smaller than a multi-shaft shredder of the same processing capacity. Small single-shaft shredders (0.1-1 ton per hour) occupy only 1-3 square meters and are approximately 1.5-2.5 meters high. Medium-sized single-shaft shredders (1-5 tons per hour) occupy approximately 3-6 square meters and are approximately 2.5-3.5 meters high. This compact size allows for flexible placement in confined spaces, such as corners in small and medium-sized plastic recycling plants, community waste disposal stations, and restaurant kitchens.
In contrast, a dual-shaft shredder of the same processing capacity occupies approximately 1.5-2 times the floor space of a single-shaft shredder, and a quad-shaft shredder occupies 2-3 times the floor space, making it difficult to fit into confined spaces. For example, a community waste disposal station needs to process waste plastic film and woven bags generated by residents. With only 5 square meters of space, a small single-shaft shredder can meet this need; a dual-shaft shredder would be impossible to install.
Core Advantages of Single-Shaft Shredders: Practical Value in Specific Scenarios
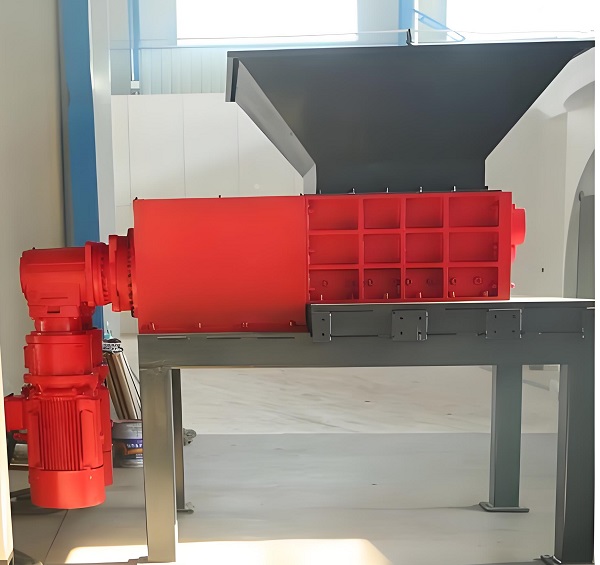
The technical features of single-shaft shredders give them significant advantages in the shredding of tough and flexible materials. These advantages are reflected not only in the performance of the equipment itself but also in improved efficiency, reduced costs, and easier operation in practice. Considering the application scenarios across various industries, their core advantages can be summarized in the following four aspects:
1. Outstanding Tough/Flexible Material Handling Capability, Solving the "Entanglement Problem"
In both industrial production and daily life, shredding tough/flexible materials such as plastic film, woven bags, waste fabric, rubber hoses, and fishing nets presents a significant challenge. These materials are soft and ductile, easily entangled in the shafts of multi-shaft shredders, causing equipment jams, downtime, and even damage to the cutting tools. The single-shaft shredder, with its "spiral blade + directional conveying" design, perfectly solves this problem, becoming a specialized device for processing this type of material.
For example, in the plastic film recycling industry, a plastics recycling plant previously used a dual-shaft shredder to process waste greenhouse film. Due to film entanglement around the shafts, the shredder required 2-3 stops per hour for cleaning, resulting in a processing capacity of only 0.5 tons per hour. After switching to a single-shaft shredder, the film was entangled throughout the directional conveying process using the spiral blades, increasing the processing capacity to 1.5 tons per hour and improving the effective operating time from 60% to 95%. Furthermore, in the textile industry, single-shaft shredders can shred waste fabric and yarn into uniform fibers, preventing them from entanglement and providing high-quality raw materials for subsequent recycled textiles.
2. Highly uniform crushed particles improve subsequent processing efficiency.
For applications where crushed materials must be fed directly to the next process (such as plastic pelletizing, recycled textiles, and biomass fuel production), the uniformity of crushed particles directly impacts subsequent processing efficiency and product quality. The single-shaft shredder's "precise gap + spiral blade assembly" design ensures consistent shredded pellet size, eliminating the need for subsequent screening and significantly improving overall production efficiency.
For example, in plastic recycling and pelletizing, uneven shredded plastic pellets can lead to incomplete melting and unstable pellet formation during the pelletizing process, necessitating a time-consuming and labor-intensive screening step (either manual or machine-based). A plastic pelletizing plant uses a single-shaft shredder to process waste plastic bottles. The resulting pellets have a size deviation of ≤±1mm and can be fed directly into the pelletizer without screening, increasing pelletizing efficiency by 20% and reducing labor costs associated with the screening process (saving approximately 50,000 yuan annually).
In biomass fuel production, flexible biomass materials such as straw and rice straw must be shredded to a uniform particle size (typically 5-10mm) to ensure pelletizing efficiency and combustion performance. A single-shaft shredder can shred straw into uniform pellets, preventing pelletizer blockage caused by uneven particle size and improving pelletizing efficiency by 15%-25%.

3. Low operating costs, suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises and budget-constrained scenarios
For small and medium-sized enterprises, individual businesses, or projects with limited budgets, equipment operating costs (including purchase, maintenance, energy, and labor) are key considerations. Single-shaft shredders offer significant advantages in this regard:
Low purchase costs: Single-shaft shredders have a streamlined structure and low manufacturing costs, making them significantly cheaper than multi-shaft shredders of the same capacity. Small single-shaft shredders (0.1-1 ton per hour) cost approximately 20,000-100,000 RMB, while medium-sized units (1-5 tons per hour) cost approximately 100,000-300,000 RMB. Dual-shaft shredders of the same capacity cost approximately 50,000-200,000 RMB (small) and 200,000-600,000 RMB (medium), with quad-shaft shredders costing even more.
Low maintenance costs: As mentioned above, the blade replacement cost and maintenance time for a single-shaft shredder are only 50%-70% of those for a dual-shaft shredder, saving an average of 10,000-50,000 RMB in annual maintenance costs. Low energy and labor costs: Single-shaft shredders have relatively low motor power (1.5-11kW for small units, 11-37kW for medium-sized units). They consume approximately 10-20 kWh of energy to process one ton of material, lower than a double-shaft shredder (15-25 kWh). Furthermore, single-shaft shredders are highly automated, equipped with a PLC control system that automatically feeds, shreds, and protects against overload. They eliminate the need for dedicated personnel, requiring only regular inspections, saving 30,000-80,000 yuan in labor costs annually.
For example, a plastics recycler with a budget of 100,000 yuan and a need to process waste plastic film and woven bags could choose a small single-shaft shredder (priced at 80,000 yuan) to meet their needs, with average annual operating costs (energy consumption + maintenance + labor) of approximately 20,000 yuan. A double-shaft shredder with the same processing capacity (priced at 150,000 yuan) would exceed their budget and incur average annual operating costs of approximately 35,000 yuan, making the single-shaft shredder more cost-effective.
4. Convenient Operation and High Mobility, Suitable for Flexible Operations in Multiple Scenarios
The single-shaft shredder's ease of operation and mobility make it suitable for diverse and flexible operations, particularly those requiring frequent relocation or on-site shredding.
Convenient Operation: The single-shaft shredder's user-friendly control system features a touchscreen and simple buttons, allowing operators to independently operate it after just 1-2 hours of training. The machine's spacious feed port allows for manual or conveyor feeding, eliminating the need for complex feed adjustments.
High Mobility: Some small single-shaft shredders are equipped with universal wheels and a traction device, allowing them to be transported by forklift or truck for on-site shredding. For example, in landscaping waste disposal, a single-shaft shredder can be transported to the site to shred branches, leaves, and weeds directly, eliminating material transportation costs. After large-scale exhibitions or events, a single-shaft shredder can be brought to the site to shred waste posters, banners, and other paper and plastic materials, achieving local processing and reduced transportation.
Furthermore, single-shaft shredders are quieter (typically operating below 80dB), significantly quieter than dual-shaft shredders (85-95dB) and quad-shaft shredders (90-100dB). They are suitable for noise-sensitive locations (such as waste disposal stations near communities, schools, and hospitals), minimizing their impact on the surrounding environment.

While single-shaft shredders lack the crushing hardness and processing volume of multi-shaft shredders, their exceptional performance in crushing tough and flexible materials makes them an indispensable component of industrial solid waste treatment and resource recovery systems. Their core advantages of anti-entanglement, high uniformity, low cost, and ease of operation perfectly meet the shredding needs of small and medium-sized enterprises, individual businesses, and those with limited space, providing efficient solutions for niche industries such as plastic recycling, textile regeneration, and biomass processing.
With the continued advancement of environmental protection policies and the growing demand for resource recycling, single-shaft shredders will play a greater role in technological upgrades and the expansion of their application areas. When selecting a shredder, companies need to make a rational choice based on their own material characteristics, processing scale, and budget to fully realize the value of the single-shaft shredder and achieve the goal of "efficient crushing, cost reduction, and efficiency improvement."
Save Time! Get A Detailed Quotation Quickly.
