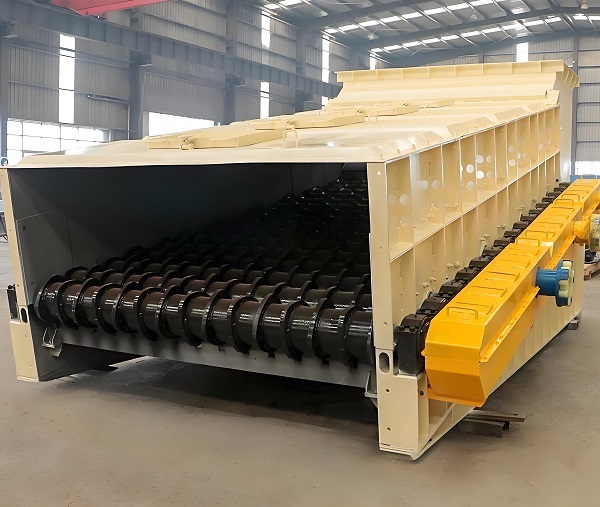

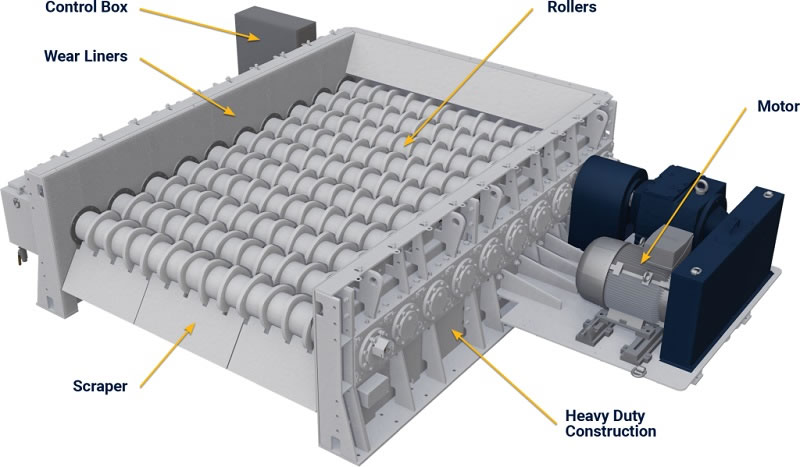
The disc screen is a solid waste sorting equipment with a rotating disc group as the core, which separates materials through the gaps between the discs. It is suitable for domestic waste and stale waste, has good anti-blocking properties, and is mostly used for sorting coarse and fine materials in waste resource processing.
The disc screen is a highly efficient device designed specifically for solid waste sorting. Its core structure consists of multiple sets of parallel rotating discs with adjustable gaps between them. The disc screen is suitable for a variety of solid waste materials, including household waste, stale waste, and construction waste. It is primarily used for separating coarse and fine materials and is a key device in solid waste resource recovery.
Its operating principle revolves around the synergistic effect of the rotating discs: solid waste to be sorted is evenly conveyed to the top of the disc array via a feeder. As the discs rotate synchronously, fine material (such as soil and debris) with a particle size smaller than the disc gaps falls through the gaps and enters the fine material collection channel. Coarse material (such as plastic blocks and bricks and stones) with a particle size larger than the gaps is driven forward by the rotating discs and ultimately discharged through the coarse material outlet, achieving efficient separation of coarse and fine materials.
Compared to traditional screening equipment, the disc screen offers superior anti-clogging properties – the rotating discs continuously stir the material, preventing wet and sticky materials from adhering and accumulating. Furthermore, the disc gaps can be flexibly adjusted based on material characteristics to meet diverse sorting needs. It is currently widely used in scenarios such as pretreatment of domestic waste incineration, excavation and sorting of stale waste landfills, and recycling of construction waste, helping to improve solid waste sorting efficiency and resource recycling rate.

1. Determine parameters based on the material to be sorted: Identify the solid waste type (e.g., household waste/construction waste) and the particle size of the coarse and fine materials, and select a machine with a flexibly adjustable disc gap to ensure it meets your sorting needs.
2. Focus on disc material and design: Prefer wear-resistant alloy or polyurethane discs, with smooth surfaces and a well-arranged disc layout to reduce material adhesion and extend service life.
3. Select specifications based on production capacity and application scenarios: Choose a large unit for landfills with high processing capacity, and a compact unit for small recycling plants, ensuring that the equipment's processing capacity matches the actual operational intensity.
4. Verify the stability of the drive system: Choose a model with a synchronous drive and low operating noise to ensure a uniform disc rotation speed and avoid drive failures that could affect sorting accuracy and efficiency.
5. Focus on anti-clogging and cleaning features: Prefer models with automatic material removal devices, especially when processing wet, sticky, and stale waste. This reduces manual cleaning and ensures continuous operation.
6. Refer to the manufacturer's strength and after-sales service: Choose a manufacturer with solid waste treatment experience, and confirm that they provide trial operation, installation and commissioning, and supply of wearing parts to reduce the risk of subsequent maintenance.
The disc is made of wear-resistant material, and the drive system is precise and durable; the structure is stable and impact-resistant, with few operating failures, and it can maintain stable sorting performance while processing solid waste for a long time.
It can be customized as needed, the disc gap can be adjusted according to the type of solid waste, the equipment specifications can be changed according to production capacity, and an automatic cleaning function can be added to adapt to garbage, construction waste and other processing scenarios.
It has high sorting efficiency and can quickly separate coarse and fine materials; it is suitable for wet and sticky solid waste without clogging, operates stably and with low noise, and can meet the needs of garbage disposal and other scenarios in the long term.
The disc screen is centered around a rotating disc assembly, with adjustable gaps to accommodate different types of solid waste. It has excellent anti-clogging properties and can handle wet and sticky materials. It also boasts high sorting efficiency and low noise, making it widely used for separating coarse and fine waste.




The disc screen's operating principle is centered around a rotating disc assembly and gap classification. It achieves efficient separation of coarse and fine solid waste through mechanical linkage. The specific process can be divided into three steps:
First, the power drive and structural linkage. A synchronized drive system drives the rotation of multiple sets of parallel discs. Adjustable gaps are provided between the discs (set according to sorting requirements), and the entire screen surface is slightly inclined, providing the basic power for material conveying and separation.
Second, the core sorting stage. Solid waste, such as household waste and stale garbage, is evenly spread onto the rotating disc assembly through a feed device. Fine material (such as soil and debris), whose particle size is smaller than the disc gaps, falls through the gaps driven by the rotation of the discs and enters the fine material collection channel. Coarse material (such as plastic blocks and bricks and stones), whose particle size is larger than the gaps, is continuously pushed forward by the rotating discs and ultimately discharged from the coarse material outlet, completing the coarse and fine material separation.
Finally, there is anti-clogging protection. The disc will continuously turn the material during rotation to prevent wet and sticky materials from adhering and accumulating. At the same time, the disc surface of some models is designed to be smooth, further reducing the risk of clogging and ensuring that the equipment can still operate stably when processing high-humidity solid waste, and continue to complete the sorting operation efficiently.

| No. | Model | Disc Diameter (mm) | Screen Length (mm) | Layers | Capacity (t/h) | Motor Power (kW) | Disc Speed (r/min) | Dimensions (mm) | Weight (kg) | Applicable Materials |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DP-800 | 300 | 2000 | 1 | 5–10 | 3 | 50–80 | 2800 × 1200 × 1200 | 950 | Wood chips, pulp residue, light solid waste |
| 2 | DP-1000 | 350 | 2500 | 1 | 8–15 | 4 | 50–80 | 3200 × 1300 × 1300 | 1100 | Household waste, plastic film, sawdust |
| 3 | DP-1200 | 400 | 3000 | 1 | 10–20 | 5.5 | 45–70 | 3600 × 1500 × 1400 | 1400 | Municipal solid waste, recyclable materials |
| 4 | DP-1500 | 450 | 3500 | 1 | 15–30 | 7.5 | 40–60 | 4000 × 1700 × 1500 | 1850 | Construction waste, paper pulp, plastic bottles |
| 5 | DP-1800 | 500 | 4000 | 1 | 20–40 | 11 | 35–55 | 4600 × 1900 × 1600 | 2400 | Waste paper, wood blocks, organic waste |
| 6 | DP-2000 | 550 | 4500 | 1 | 30–50 | 15 | 30–50 | 5000 × 2100 × 1700 | 2800 | Industrial waste, plastic separation |
| 7 | DP-2400 | 600 | 5000 | 1 | 40–70 | 18.5 | 25–45 | 5500 × 2300 × 1800 | 3300 | Bulk waste, construction mixed materials |
*The output will vary according to different materials, feed particle size and other factors.
Save Time! Get A Detailed Quotation Quickly.
